字符串必须包含在一对双引号""内
声明字符串变量必须经过初始化才能使用,否则会报变量未被初始化错误
创建
String s1 = “hello,world”; // 推荐
String s2 = new String(“hello,world”);
拼接
+连接字符串; // 字符串太长时,可以通过+号将字符串分两行显示
长度
获取字符串长度:str.length(); //空格和其他转义字符均计算为长度1
查找
① str.indexOf(subStr); //找到则返回subStr首次出现在str中的索引位置,没有查找到则返回-1
② str.lastIndexOf(subStr); //找到则返回subStr最后一次出现在str中的索引位置,没有查找到则返回-1; subStr为””空字符串则效果等同于str.length()
获取指定所以你位置的字符
str.charAt(index); // 将指定索引处的字符返回
比较
str.compareTo(otherstr); // 按字典顺序对比,如果str位于参数字符串之前,则返回为一个负整数;若位于之后,则返回一个正整数;若字符串相等,则结果为0
替换
str.replace(oldChar, newChar); // 将指定的字符或字符串全部替换成新的字符或字符串,返回字符串副本
分割
str.split(regex); // regex为正则表达式;返回值为 String[] 类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class TestDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "192.168.0.1";
String[] firstArrays = str.split("\\.");
for (String a : firstArrays) {
System.out.print(a + " ");
}
}
}
|
子字符串
① str.substring(beginIndex); // 返回从指定索引位置开始截取到字符串结尾的子串
② str.substring(beginIndx, endIndex); // 返回从指定索引位置开始到指定位置结束的子串
去除空格
str.trim(); // 返回字符串的副本,忽略首部和尾部所有空格
首尾判断
① str.startsWith(String prefix); // 判断当前字符串对象的前缀是否为参数指定的字符串
② str.endsWith(String suffix); // 判断当前字符串对象的后缀是否为参数指定的字符串
相等判断
① str.equals(otherstr); // 比较str和otherstr字符串内容和长度,返回boolean类型,相等true,不等false
② str.equalsIgnoreCase(otherstr); // 忽略大小写比较str和otherstr字符串内容和长度,返回boolean类型,相等true,不等false
大小写转换
str.toLowerCase(); // 返回一个新字符串,将str所有字符转换为小写
str.toUpperCase(); // 返回一个新字符串,将str所有字符转换为大写
日期格式化
静态format()方法
str.format(string format, Object…args); // 创建格式化的字符串,使用指定格式字符串和参数返回一个格式化字符串。
日期和时间字符串格式化
String s = String.format(“%te”, new Date()); // 返回当月截止当天的天数


1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
| import java.util.Date;
public class TestDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();
String[] s1 = new String[11];
s1[0] = String.format("%te", date);
s1[1] = String.format("%tb", date);
s1[2] = String.format("%tB", date);
s1[3] = String.format("%ta", date);
s1[4] = String.format("%tA", date);
s1[5] = String.format("%tY", date);
s1[6] = String.format("%ty", date);
s1[7] = String.format("%tj", date);
s1[8] = String.format("%tm", date);
s1[9] = String.format("%td", date);
s1[10] = String.format("%tc", date);
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length; i++) {
System.out.println("s1[" + i + "]: " + s1[i]);
}
System.out.println(" ------------------------------------------------------ ");
String[] s2 = new String[13];
s2[0] = String.format("%tH", date);
s2[1] = String.format("%tI", date);
s2[2] = String.format("%tk", date);
s2[3] = String.format("%tl", date);
s2[4] = String.format("%tM", date);
s2[5] = String.format("%tS", date);
s2[6] = String.format("%tL", date);
s2[7] = String.format("%tN", date);
s2[8] = String.format("%tp", date);
s2[9] = String.format("%tz", date);
s2[10] = String.format("%tZ", date);
s2[11] = String.format("%ts", date);
s2[12] = String.format("%tQ", date);
for (int i = 0; i < s2.length; i++) {
System.out.println("s2[" + i + "]: " + s2[i]);
}
System.out.println(" ------------------------------------------------------ ");
System.out.println(s1[5] + "/" + s1[8] + "/" + s1[9] + " "
+ s2[0] + ":" + s2[4] + ":" + s2[5]);
System.out.println(" ----------------常见日期和时间格式化组合---------------- ");
System.out.println("全部信息 :" + String.format("%tc", date));
System.out.println("年-月-日 :" + String.format("%tF", date));
System.out.println("月/日/年 :" + String.format("%tD", date));
System.out.println("时:分 :" + String.format("%tR", date));
System.out.println("时:分:秒 :" + String.format("%tT", date));
System.out.println("时:分:秒 PM/AM :" + String.format("%tr", date));
}
}
|
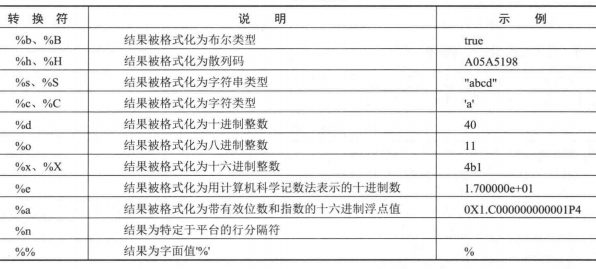
常规类型格式化(大部分与C语言占位符相同)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public class TestDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = String.format("%d", 10/3);
String s2 = String.format("%b", 10 > 3);
String s3 = String.format("%08x", 31);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println("0x" + s3);
}
}
|