06-线程安全集合
1. Collection体系下线程安全集合
Collection体系集合下,除Vector以外的线程安全集合(蓝色):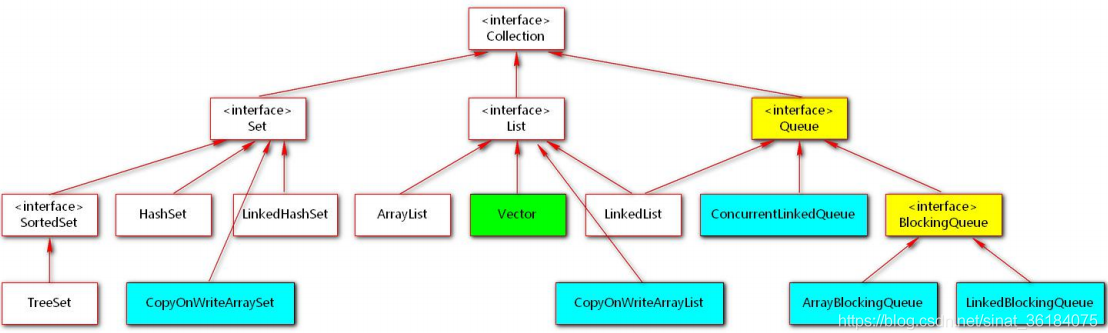
Collections工具类中提供了多个可以获得线程安全集合的方法:
public static <T> Collection<T> synchronizedCollection(Collection<T> c)
public static <T> List<T> synchronizedList(List<T> list)
public static <T> Set<T> synchronizedSet(Set<T> s)
public static <K,V> Map<K,V> synchronizedMap(Map<K,V> m)
public static <T> SortedSet<T> synchronizedSortSet(SortedSet<T> s)
public static <K,V> SortedMap<K,V> synchronizedSortedMap(SortedMap<K,V> m)
特点:
- 都是返回对应泛型集合类型的方法;
- 都是静态方法,通过Collections直接调用;
- 都是在静态方法中new了一个synchronized同步的静态内部类;
- 实际使用时的成员方法与原集合没有区别;
- JDK1.2提供,接口统一、维护性高,但性能没有提升,均以synchonized实现。
示例其中一个:
1 | |
2. CopyOnWriteArrayList类(线程安全的List)
1 | |
说明:
- 符合List特点:有序、有下标、元素可重复
- 线程安全的ArrayList,加强版读写分离;
- 写有锁,读无锁,读写之间不阻塞,优先读写锁;
- 写入时,先copy一个容器副本、再添加新元素,最后替换引用;
- 使用方式与ArrayList无异。
1 | |
3. CopyOnWriteArraySet类(线程安全的Set)
1 | |
说明:
- 符合Set特点:无序、无下标、元素不重复
- 线程安全的Set,底层使用CopyOnWriteArrayList实现;
- 唯一不同在于,使用addIfAbsent()添加元素(查重),会遍历数组;
- 如存在元素,则不添加(扔掉副本)。
1 | |
4. ConcurrentHashMap类(线程安全的Map)
1 | |
说明:
- 初识容量默认为16段(Segment),使用分段锁设计;
- 不对整个Map加锁,而是为每个Segment加锁;
- 当多个对象存入同一个Segment时,才需要互斥;
- 最理想状态位16个对象分别存入16个Segment,并行线程数量16个;
- 使用方式与HashMap无异。
// JDK1.7: 分段锁设计 Segment
// JDK1.8: CAS交换算法(CAS比较和交换) + 同步锁(锁的是表头)
1 | |
**CAS交换算法(Compare And Swap)**:
V:要更新的变量
E:预期值
N:新值
当 V == E 时,V=N;
如果在修改过程中,V已经发生了变化,V != E,则取消当前赋值操作,做下一次赋值。
1 | |
补充:对ConcurrentHashMap的线程安全算法理解
源码分析:
JDK1.7中ConcurrentHashMap中的putVal()实现方式:分段锁 Segment(16把锁)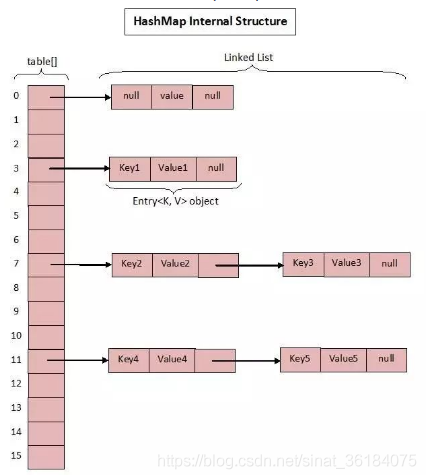
JDK1.8中ConcurrentHashMap中的putVal()实现方式:【CAS交换算法 + 同步锁】锁链表表头对象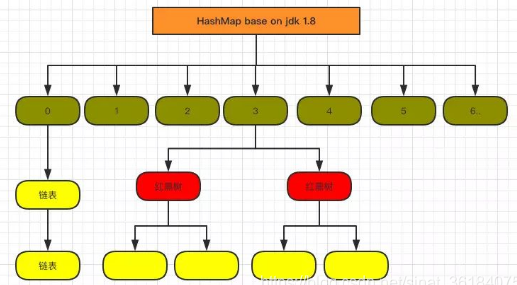
JDK1.8源码分析 - 当我们调用put方法时,CAS交换算法+同步锁是如何保证线程安全的:
1 | |

06-线程安全集合
https://janycode.github.io/2016/04/28/02_编程语言/01_Java/01_JavaSE/03_泛型集合/06-线程安全集合/