1. JDBC 封装连接数据库工具类
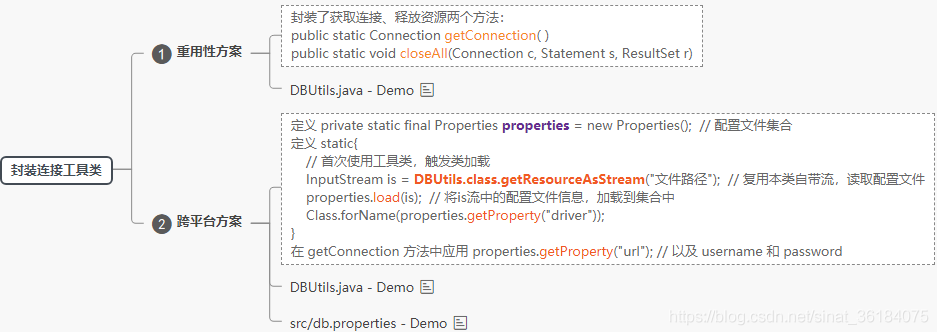
1.1 可重用方式
封装了获取连接、释放资源两个方法:
public static Connection getConnection( )
public static void closeAll(Connection c, Statement s, ResultSet r)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
public class DBUtils {
static {
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Connection getConnection() {
Connection connection = null;
try {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/companydb?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "admin123");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return connection;
}
public void closeAll(Connection c, Statement s, ResultSet r) {
try {
if (r != null) {
r.close();
}
if (s != null) {
s.close();
}
if (c != null) {
c.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
1.2 跨平台方式
1
2
3
4
5
|
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql:
username=root
password=123456
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| ```java
public class DBUtils {
private static final Properties properties = new Properties();
static {
try {
InputStream is = DBUtils.class.getResourceAsStream("/db.properties");
properties.load(is);
Class.forName(properties.getProperty("driver"));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(properties.getProperty("url"), properties.getProperty("username"), properties.getProperty("password"));
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return connection;
}
public static void closeAll(Connection c, Statement s, ResultSet r) {
try {
if (r != null) {
r.close();
}
if (s != null) {
s.close();
}
if (c != null) {
c.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
2. JDBC 封装数据访问
2.1 ORM 思想
概念:Object Relational Mapping,对象关系映射。
将数据库查询到的结果集遍历映射为对象集合。
ORM entity规则:表名=类名;列名=属性名;提供各个属性的get/set方法;提供无参构造和[若需有参构造]。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String sex;
private String email;
private String address;
}
public class OrmSelect {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = DBUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
String sql = "select id, username, passwrod, sex, email, address from user";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String username = resultSet.getString("username");
String password = resultSet.getString("passwrod");
String sex = resultSet.getString("sex");
String email = resultSet.getString("email");
String address = resultSet.getString("address");
User user = new User();
user.setId(id);
user.setUsername(username);
user.setPassword(password);
user.setSex(sex);
user.setEmail(email);
user.setAddress(address);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
|
2.2 DAO 层
概念:Data Access Object,数据访问对象。
- 将所有对同一张表的操作(增删改查)都封装在一个
XXXDaoImpl 对象中;
- 根据增删改查的不同功能,实现具体的方法(
insert, update, delete, select, selectAll);
经验:应将对于一张表的所有操作统一封装在一个数据访问对象中。——重用!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
class Stu {
private String student_id;
private String student_name;
private String sex;
private Date birthday;
private String phone;
private int gradeId;
}
public class StuDaoImpl {
private Connection connection = null;
private PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
private ResultSet resultSet = null;
public int insert(Stu stu) {
connection = DBUtils.getConnection();
String sql;
sql = "insert into stu(student_id, student_name, sex, birthday, phone, gradeId) values(?,?,?,?,?,?)";
try {
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, stu.getStudent_id());
preparedStatement.setString(2, stu.getStudent_name());
preparedStatement.setString(3, stu.getSex());
preparedStatement.setDate(4, DateUtils.utilToSql(stu.getBirthday()));
preparedStatement.setString(5, stu.getPhone());
preparedStatement.setInt(6, stu.getGradeId());
return preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtils.closeAll(connection, preparedStatement, resultSet);
}
return 0;
}
public int delete(int id) {}
public int update(Stu stu) {}
public Stu select(int id) {}
public void selectAll() {}
}
|
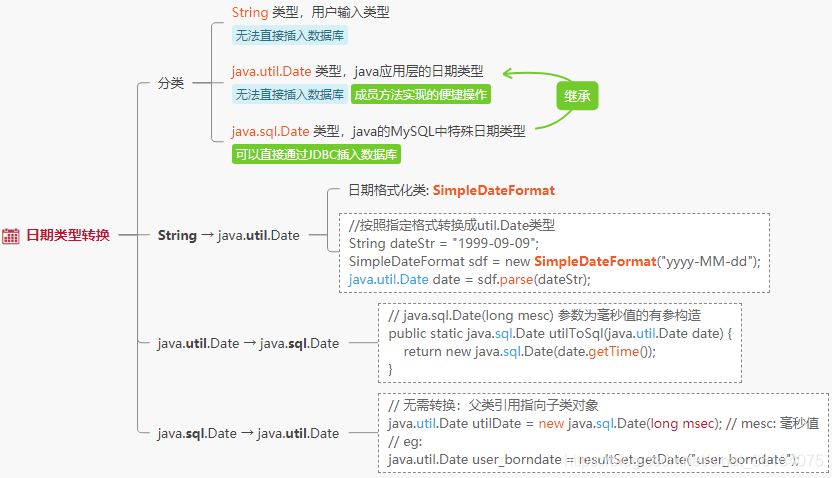
补充:String、java.util.Date、java.sql.Date 之间的转换
看我一张图,胜写10行码!