验证代码已放在 git:https://github.com/janycode/eelock.git
1. Redis分布式锁理论
Redis有一系列的命令,特点是以NX结尾,NX是Not eXists的缩写,如SETNX命令就应该理解为:SET if Not eXists。
设置成功,返回 1 。 设置失败,返回 0
由于Redis为单进程单线程模式,采用队列模式将并发访问变成串行访问,命令是一条一条执行的所以可以利用setNx可以实现分布式锁。
方法执行前请求redis 进行setnx命令。如果返回1,则表示此时该线程获得锁,执行方法,如果返回0,表示锁已经被占用了,等待重新获取或者超时处理。
项目依赖:spring-boot 版本2.3.0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
2. Redis整合 封装服务类
基于spring boot 封装的 RedisTemplate 实现redis 服务。
- Redis 配置:主要设置了redis 序列化的一些配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
| import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<String, Object>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
template.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
}
|
- service层编写: service 只提供2个方法加锁和解锁,加锁需要几个参数redis 里的key、value,锁的过期时间,获取锁的重试间隔时间,获取不到锁的超时时间。 解锁要两个参数锁的key 和value值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
public interface RedisService {
boolean tryLock(String key, String value, long expireTime, long timeout, long interval);
void unLock(String key, String value);
}
|
- service实现层
加锁方法: 首先判断 获取不到锁的等待时间如果小于等于0 给一个默认时间30毫秒。
如果获取不到锁超时时间大于0 就获取当前时间进行判断,是否超时
获取到锁直接返回true 获取不到锁则锁定当前线程进行等待。
这里使用redisTemplate里的方法进行redis 命令操作,需要考虑的问题:锁必须有超时时间,如果A线程获取了锁,A线程在执行过程中异常,导致永远也不会执行结束 这时候锁被A线程占用,其他线程永远获取不到锁,造成死锁。所以要根据业务处理估算时间 进行设置过期时间,如果A线程异常 则超时自动释放锁。由于setnx和expire不具备原子性,假设 用户setnx后 在expire前线程异常,则锁的过期时没有设置上,所以此处必须保证原子性。 redis版本升级到2.1以上,直接在setIfAbsent中设置过期时间,也可以是用lua脚本实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| import com.example.eelock.service.RedisService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class RedisServiceImpl implements RedisService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Override
public boolean tryLock(String key, String value, long expireTime, long timeout, long interval) {
if(interval<=0){
interval = 30L;
}
try {
if (timeout > 0) {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
while (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin < timeout) {
if (redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, value, expireTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
return true;
}
synchronized (Thread.currentThread()) {
Thread.currentThread().wait(interval);
}
}
return false;
} else {
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, value, expireTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}catch (Exception e){
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void unLock(String key, String value) {
}
}
|
解锁方法:解锁需要注意一点,解铃还须系铃人,假设A线程获取到了锁,但是正常执行了,但是执行方法耗时太长了导致超时了,锁自动释放了,此时B线程获取到了锁,B执行方法中,A执行结束 进行了释放锁, 由于没有判断 锁是否是A加的锁,进行了删除,所以B在正常未执行结束的时候锁已经被A释放了,这就造成了并发问题。所以A在解锁前要判断锁是否为A加的锁,利用redis命令存储时设置的value 进行判断是否为A加的锁,删除锁之前先获取判断后如果值和A设置的值相等进行删除操作。需要注意的是判断和删除操作必须保持原子性,在高并发情况下,如果两条命令不是原子性操作,在判断后,锁超时释放了,其他线程获取到了锁,就会被误删除。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
@Override
public void unLock(String key, String value) {
String script = "if redis.call('get', KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1] then return redis.call('del', KEYS[1]) else return 0 end";
DefaultRedisScript<Long> defaultRedisScript = new DefaultRedisScript();
defaultRedisScript.setScriptText(script);
defaultRedisScript.setResultType(Long.class);
Long res = (Long) redisTemplate.execute(defaultRedisScript, Collections.singletonList(key), value);
if (res != 1L) {
System.err.println("释放失败");
}
}
|
注意:使用redisTemplate执行脚本 和使用Jedis 执行脚本参数不一致。开始没注意,导致测试的时候 一直删除不掉锁。
看下代码:
jedis 参数为 脚本和两个集合
1
2
3
4
|
public Object eval(String script, List<String> keys, List<String> args) {
return this.eval(script, keys.size(), getParams(keys, args));
}
|
redisTemplate参数为一个集合 和多个参数代替第二个集合
1
2
3
4
|
public <T> T execute(RedisScript<T> script, List<K> keys, Object... args) {
return scriptExecutor.execute(script, keys, args);
}
|
3. 自定义注解
自定义注解:需要几个参数 锁的key,获取锁的间隔、失效时间、超时时间
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface RedisLock {
String key() default "";
long interval() default 100L;
long expireTime() default 10 * 1000L;
long timeout() default 5 * 1000L;
}
|
4. Aop实现注解环绕通知、获取注解参数、加锁解锁
Aop里需要做的事情:在方法执行前,获取锁的注解值,进行加锁,如果加锁成功进行方法执行,如果加锁失败 抛出异常,可以自定义异常使用统一异常处理。
大概是:切入注解 RedisLock ,获得注解的参数,使用uuid作为redis value,解锁的时候传入认证 封装获取key的方法,反射根据注解 执行方法 获得参数里的key值,默认为类名+方法名
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
| import com.example.eelock.anno.RedisLock;
import com.example.eelock.service.RedisService;
import com.example.eelock.util.ThreadLocalUtil;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.UUID;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LockAspect {
@Autowired
private RedisService redisService;
@Around("@annotation(com.example.eelock.anno.RedisLock)")
public Object redisLockAop(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Object res = null;
RedisLock lock = ((MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod().getAnnotation(RedisLock.class);
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
String key = getKey(joinPoint, lock.key());
System.err.println("[KEY] :" + key);
if (ThreadLocalUtil.get(key) != null) {
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
if (redisService.tryLock(key, uuid, lock.expireTime(), lock.timeout(), lock.interval())) {
ThreadLocalUtil.put(key, "");
res = joinPoint.proceed();
ThreadLocalUtil.clear(key);
redisService.unLock(key, uuid);
return res;
} else {
throw new Exception();
}
}
public String getKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, String key) {
String className = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
try {
if ("".equals(key)) {
return className + methodName;
}
if (key.startsWith("#args")) {
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
int index = Integer.parseInt(key.substring(key.indexOf("[") + 1, key.indexOf("]")));
Object keyArgs = args[index];
if (key.split("\\.").length <= 1) {
return keyArgs.toString();
}
Class<?> clas = keyArgs.getClass();
Method method = clas.getMethod(key.split("\\.")[1].split("\\(")[0]);
return method.invoke(keyArgs).toString();
}
return key;
} catch (Exception e) {
return className + methodName;
}
}
}
|
5. ThreadLocal实现可重入锁
可重入性:假设a方法需要 testlock锁,b方法也需要testlock锁,a方法调用了b方法,此时锁被a方法获取,b方法获取不到锁永远等待,所以 如果线程有一个方法获取到了锁,则其他方法不需要获取锁就可以执行了。
ThreadLocal是解决线程安全问题一个很好的思路,它通过为每个线程提供一个独立的变量副本解决了变量并发访问的冲突问题。
使用ThreadLocal,在获取到锁的时候 标记一下,方法获取锁之前先判断线程是否已经获取到锁了。
提供一个ThreadLocal 帮助类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
| import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ThreadLocalUtil {
private static final ThreadLocal<Object> tlContext = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void put(Object key, Object value) {
Map m = (Map) tlContext.get();
if (m == null) {
m = new HashMap();
tlContext.set(m);
}
m.put(key, value);
}
public static Object get(Object key) {
Map m = (Map) tlContext.get();
if (m == null) return null;
return m.get(key);
}
public static void clear(Object key) {
Map m = (Map) tlContext.get();
if (m == null) return;
m.remove(key);
}
}
|
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| package com.example.eelock.controller;
import com.example.eelock.anno.RedisLock;
import com.example.eelock.pojo.Userinfo;
import com.example.eelock.service.RedisService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.UUID;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api/redislock")
public class TestEeLock {
@Autowired
private RedisService redisService;
@RedisLock(key = "REDISLOCK_TEST")
@GetMapping("test")
public String test() {
return UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
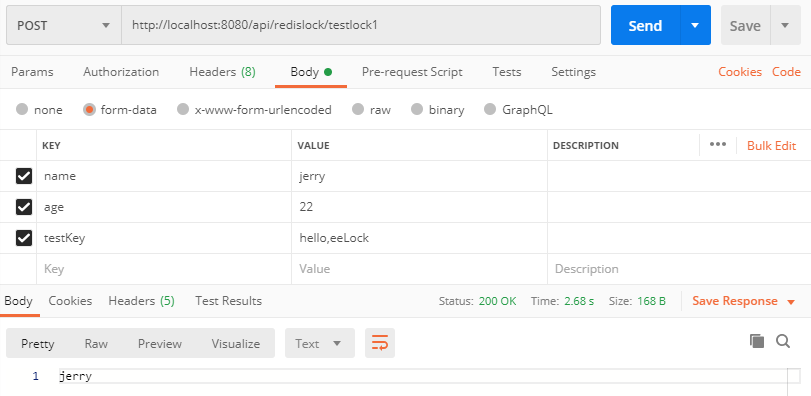
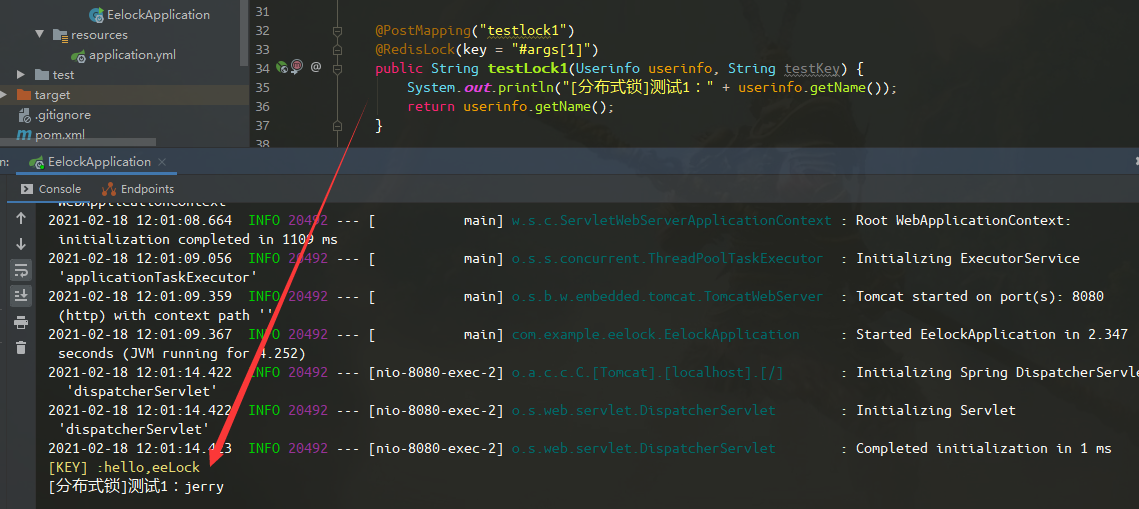
@PostMapping("testlock1")
@RedisLock(key = "#args[1]")
public String testLock1(Userinfo userinfo, String testKey) {
System.out.println("[分布式锁]测试1:" + userinfo.getName());
return userinfo.getName();
}
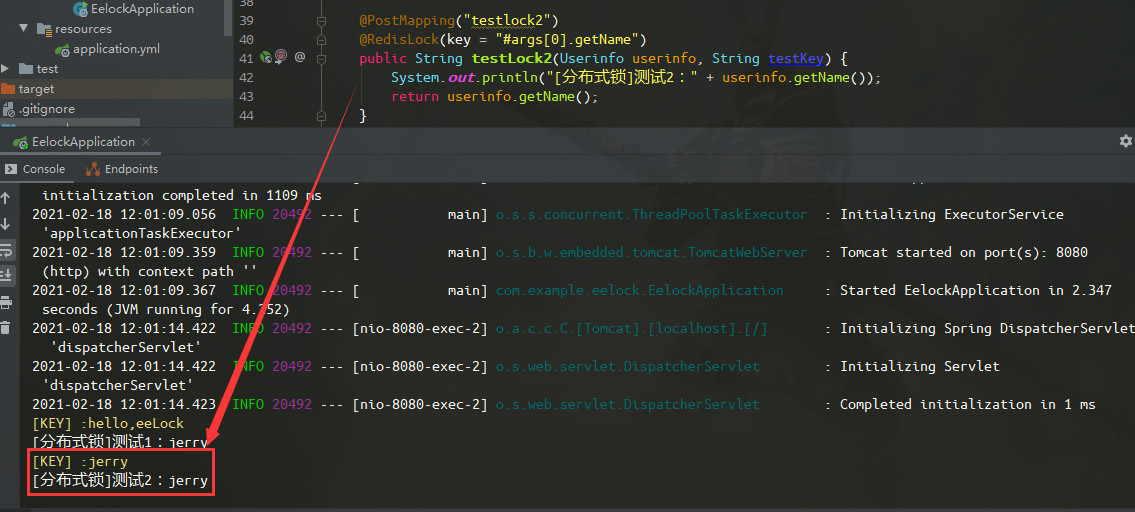
@PostMapping("testlock2")
@RedisLock(key = "#args[0].getName")
public String testLock2(Userinfo userinfo, String testKey) {
System.out.println("[分布式锁]测试2:" + userinfo.getName());
return userinfo.getName();
}
}
|
test:

testlock1:
testlock2: