
参考:
背景:
- 对象
= 引用赋值(浅拷贝),修改复制后的对象,会影响原对象
- 对象
... 展开赋值(浅拷贝+1层),只比浅拷贝多复制一层数据(只有一层结构时完全可以使用),深层的值修改还会影响原对象
- 对象
JSON.parse() 与 JSON.stringify(),可以实现深拷贝,但致命问题是:不能有 undefined 的字段值(该字段会被忽略即删除)
- 对象
deepcopy递归赋值,可以实现深拷贝,但问题是:一层一层复制,性能不好,内存占用高
1. immutable 不可变结构
介绍
Immutable.js 是一个用于创建不可变数据结构的 JavaScript 库。不可变数据一旦创建,就不能再被更改。对不可变对象的任何修改或添加删除操作都会返回一个新的不可变对象。
性能优化方式
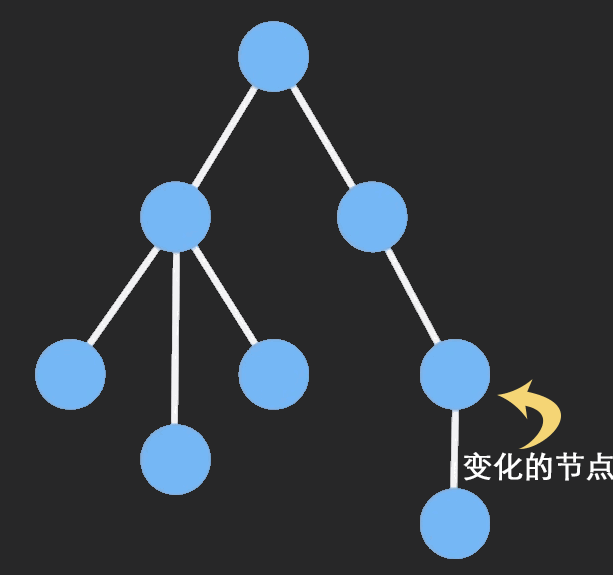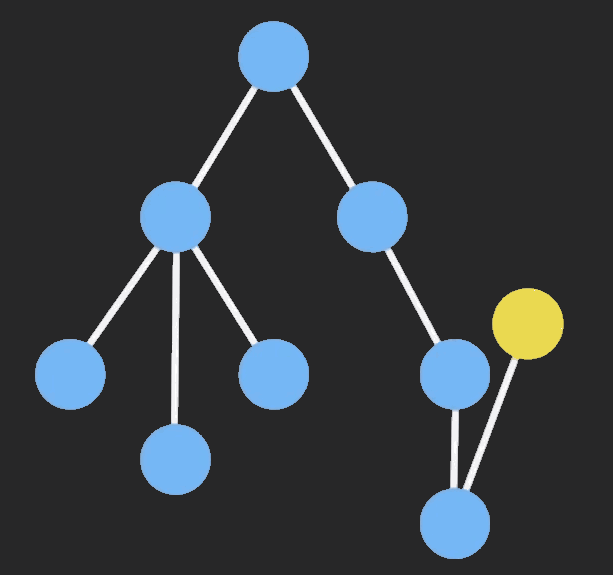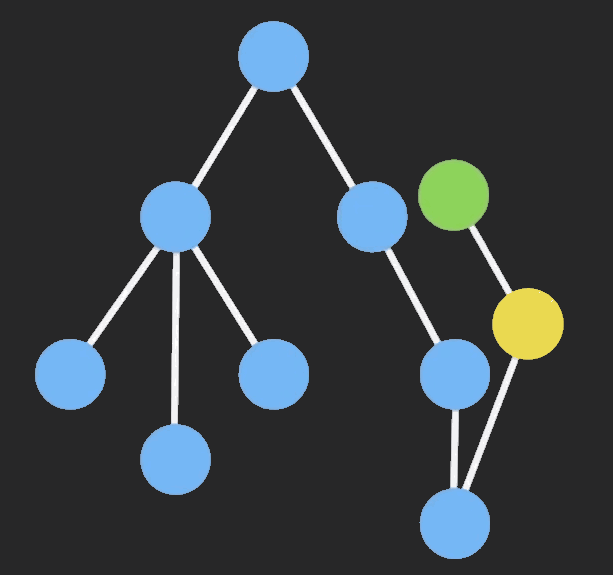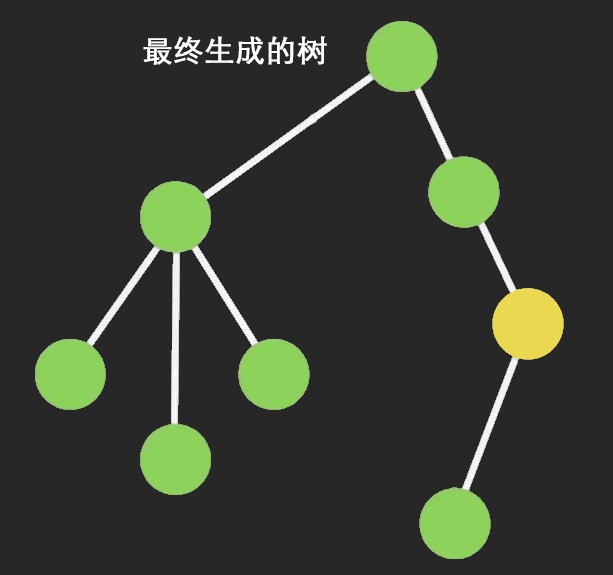
Immutable 实现的原理是 Persistent Data Structure(持久化数据结构),也就是使用旧数据创建新数据时,要保证旧数据同时可用且不变。同时为了避免 deepCopy 把所有节点都复制一遍带来的性能损耗,Immutable 使用了 Structural Sharing(结构共享),即如果对象树中一个节点发生变化,只修改这个节点和受它影响的父节点,其它节点则进行共享。
2. immutable 应用
2.1 安装
安装:npm i immutable - 最新版本 5.x
2.2 使用
Map

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| import { Map } from 'immutable'
var obj = {name: "jerry", age: 22}
const oldImmuObj = Map(obj)
const newImmuObj = oldImmuObj.set("name", "tom")
console.log(oldImmuObj, newImmuObj);
console.log(oldImmuObj.get("name"), newImmuObj.get("name"));
console.log(oldImmuObj.toJS().name, newImmuObj.toJS().name);
|
组件中使用:① 链式调用 .set(key, value) 赋值; ② 访问方式取决于是 Map 还是 toJS() 后的普通对象;③ 多层 Map 时可以直接进行判断和阻断
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
| import { Component } from 'react'
import { Map } from 'immutable'
export default class App extends Component {
state = {
info1: Map({ name: "jerry", age: 22 }),
info2: { name: "jerry", age: 22 },
info3: Map({ name: "jerry", age: 22, filter: Map({ text: "", up: true, down: false }) })
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{/* 写法1 */}
<div>
{this.state.info1.toJS().name}-{this.state.info1.toJS().age}
<button onClick={() => {
this.setState({
info1: this.state.info1.set("name", "tom").set("age", 18)
})
}}>click1</button>
</div>
{/* 写法2:与写法1效果一样 */}
<div>
{this.state.info2.name}-{this.state.info2.age}
<button onClick={() => {
let oldInfo = Map(this.state.info2)
let newInfo = oldInfo.set("name", "spike").set("age", 28)
this.setState({
info2: newInfo.toJS()
})
}}>click2</button>
</div>
{/* 复杂多层结构时的应用 */}
<div>
{this.state.info3.get("name")}
<button onClick={() => {
this.setState({
info3: this.state.info3.set("name", "tom").set("age", 18)
})
}}>click1</button>
<Child filter={this.state.info3.get("filter")} />
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
class Child extends Component {
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if (this.props.filter === nextProps.filter) {
return false
}
return true
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
console.log("componentDidUpdate");
}
render() {
return (
<div>
Child
</div>
)
}
}
|
List
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import {List} from 'immutable'
let arr1 = List([1, 2, 3])
let arr2 = arr1.push(4)
let arr3 = arr1.concat([5, 6, 7])
console.log(arr1.size);
console.log(arr2.size);
console.log(arr3.size);
|
组件中使用:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
| import { Component } from 'react'
import { List, Map, fromJS } from 'immutable'
export default class App extends Component {
state = {
info1: fromJS({
name: "jerry",
location: {
province: "广东",
city: "深圳"
},
favor: ["读书", "看报", "写代码"]
})
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log(this.state.info1);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>个人信息修改</h1>
<button onClick={() => {
this.setState({
// Map 基础修改方式
//info1: this.state.info1.set("name", "tom").set("location", this.state.info1.get("location").set("city", "广州"))
// fromJS 修改方式
info1: this.state.info1.set("name", "tom").setIn(["location", "city"], "广州")
})
}}>click</button>
<div>
{this.state.info1.get("name")}
<br />
{this.state.info1.get("location").get("province")}
-
{this.state.info1.get("location").get("city")}
<br />
<ul>
{
this.state.info1.get("favor").map((item, index) =>
<li key={item}>{item}<button onClick={() => {
console.log(index);
this.setState({
// List 基础修改方式
//info1: this.state.info1.set("favor", this.state.info1.get("favor").splice(index, 1))
// fromJS 修改方式 + 列表删除方式
// info1: this.state.info1.setIn(["favor", index], "1111")
info1: this.state.info1.updateIn(["favor"], (list) => list.splice(index, 1))
})
}}>del</button></li>
)
}
</ul>
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
|
fromJS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| const nested = fromJS({ a: { b: { c: [3, 4, 5] } } });
const nested2 = nested.mergeDeep({ a: { b: { d: 6 } } });
console.log(nested2.getIn(['a', 'b', 'd']));
getIn(["a", "b", "c"])
const nested3 = nested2.setIn(['a', 'b', 'd'], "jerry");
const nested4 = nested2.updateIn(['a', 'b', 'd'], value => value + 1);
console.log(nested4);
const nested5 = nested4.updateIn(['a', 'b', 'c'], list => list.push(6));
|
3. immutable + Redux
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import { fromJS } from "immutable"
const initialState = fromJS({
category: "",
material: ""
})
const reducer = (prevstate = initialState, action = {}) => {
let { type, payload } = action
switch (type) {
case GET_HOME:
var newstate = prevstate.set("category", fromJS(payload.category))
var newstate2 = newstate.set("material", fromJS(payload.material))
return newstate2;
default:
return prevstate
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
category: state.homeReducer.getIn(["category"]) || Map({}),
material: state.homeReducer.getIn(["material"]) || Map({})
}
}
this.props.category.get("相关属性")
this.props.category.toJS()
|
缺点:



